“In computer science
Big O notationis useful in the analysis of algorithms” - wikipedia.org
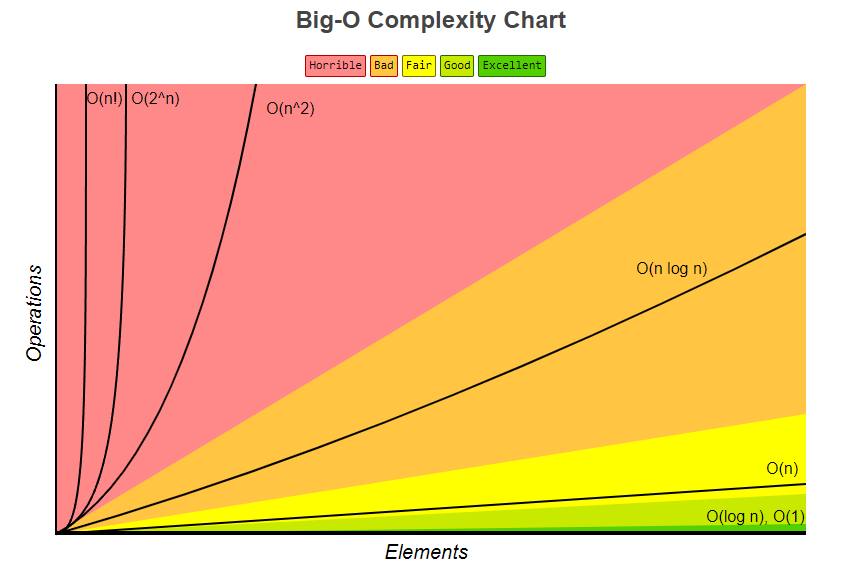
This illustation is from https://www.bigocheatsheet.com/ and is the most popular I’ve seen online.
1 | O(1) Constant Looking up by index, no matter the array size it will always take the same amount of time |
Definition
- Simplified analysis of an alorithms efficiency / time complexity.
One of my peers once explained this to me as being able to use this in regards to problem solving.
Example: what’s the big O of xs.map(...).filter(...).find(...)
What Is Big O?
- Complexity in terms of the input size,
n. How well will the algorithm perform as its input size grows. - Abstract the efficiency of our algorithms or code from the machine (its independent)
- Examine the basic computer steps of the code
- Can analyze both
time complexity(how long it takes to run) andspace complexity(how much memory it needs)
Types of measurement
Typically look at worst case but we have to be cognizant of best and average case, its dependant on the application/algorithm
- Worst case (typically used)
- Best case
- Average case
General rules
- Ignore constants for trivial examples, example a running time of
5n, it runs on the order ofO(n). This is because asngets large the 5 no longer matters- in practice constants matter, a constant of 2 or 3 could have a large impact
- The same way as
ngrows certain termsdominateothers.- Example
O(1) < O(log n) < O(n) < O(n log n) < O(n^2) < O(2^n) < O(n!) - this means we ignore/drop lower order terms when dominated
- Example
O(1) Constant time / complexity
Complexity: Excellent
Independent of input size n it takes a constant time to complete. Like 14 nanoseconds, or three minutes no matter the amount of data in the set.
1 | x = 5 + (15 * 20); ~ O(1) big O of 1 |
Sequence of statements in constant time
1 | x = 5 + (15 * 20); ~ O(1) |
O(log n) Logarithmic time / complexity
Complexity: Good
“The best way to wrap your head around this is to remember the concept of halving: every time n increases by an amount k, the time or space increases by k/2.”
An example of this is binary search, see Invert A Binary Tree (BST).
O(n) Linear time / complexity
Complexity: Fair
Increases linearly and in direct proportion to the number of inputs.
1 | for x in range (O, n): |
1 | y = 5 + (15 * 20); ~ O(1) |
O(n log n) loglinear complexity
Complexity: Bad
O(n log n) grows logarithmically, which means that the time it takes to run the algorithm will increase slowly as the input size increases.
“
O(n log n)implies thatlog noperations will occurntimes.”
O(n^2) quadratic time / exponential time
Complexity: Horrible
O(n^2) grows quadratically, which means that the time it takes to run the algorithm will increase much more quickly as the input size increases.
It takes n*n operations, example is a nested loop.
With Big O we usually look at worst case scenario, for the examples below the largest runtimes are O(n^2)
1 | x = 5 + (15 * 20); ~ O(1) |
Additionally we can have O(nˣ) or polynomial complexity which is just a range of possible values that x could be, generally for ccomputer science we are talking about x being 2.
O(2^n)
Complexity: Horrible
O(n!) factorial
Complexity: Horrible
“O(n!), or factorial complexity, is the “worst” standard complexity that exists. To illustrate how fast factorial solutions will blow up in size, a standard deck of cards has 52 cards, with 52! possible orderings of cards after shuffling.”
Additional Concepts
When I was researching Big O notation these concepts came up a lot specifically in content from Clément Mihailescu Co-Founder of https://www.algoexpert.io/
Sliding Window Technique
Involves manipulating two pointers or two indices at the same time as you’re traversing thought something like a string or an array. Basically you have a left pointer/index and a right pointer/index and your move them simultaneously in an array or a string. (could be to count frequency of characters)
Recursion
A lot of problems can be solved easily with recursion (as apposed to iteratively). This produces cleaner and less code than an iterative approach. Example problems that help you understand recursion include:
n fibonaccicalculate height of binary treeor thedepths of nodes in a binary tree
Dynamic Programming (DP)
It means being able to solve a problem that is complex by first solving a smaller version of that problem. To solve that small version of the problem you solve an even smaller version of that problem, until you can solve a trivial version of the problem. The only way to get good at DP is to do a lot of DP!
References
- Big-O notation in 5 minutes — The basics
- Big-O Notation in 100 Seconds — Fireship
- Big-O Notation - For Coding Interviews — NeetCode
- Linear Time vs. Logarithmic Time — Big O Notation
- Big O notation - wikipedia.org
- bigocheatsheet.com
- Big O Notation and Time/Space Complexity - medium.com
- What is Big O notation? And why do we need it? - medium.com