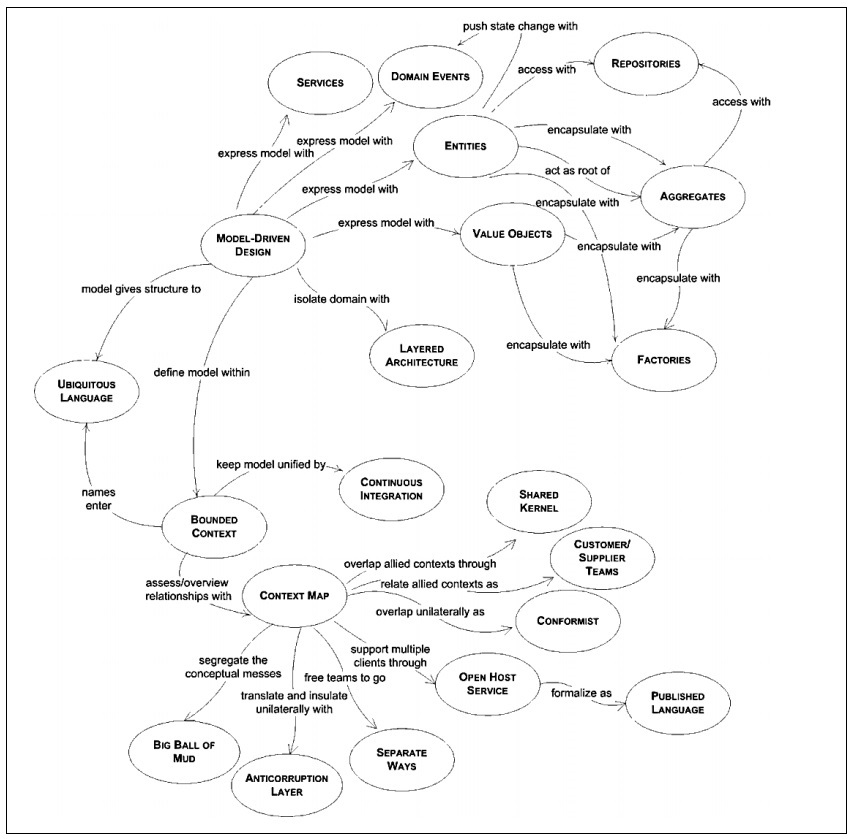
An attempt to try understand what Domain Driven Design (DDD) is and how I can apply its practice and principles. Eric Evans defines a navigation map for DDD reference:
General Terms
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Problem Domain | The specific problem the software you’re working on is trying to solve. |
| Core Domain | The key differentiator for the customer’s business – something they must do well and cannot outsource. |
| Ubiquitous Language | Common language used by domain experts and developers. |
| Sub Domain | Divide each problem of the application into a sub-domain, Examples: Sales, Accounting & Marketing are separate concerns. These are separate applications or features your software must support or interact with. |
| Bounded Context | A description of a boundary (typically a subsystem, or the work of a particular team) within which a particular model is defined and applicable. Its ok for the same entity to have a different meaning per context in the same domain. Example: Customer - for a Sales Bounded Context this could be a Lead. For the Bookings Bounded Context this could be a Passenger. |
| Context Maps | Used to visualize/demonstrate where the boundaries between contexts lie. This is the The process of identifying bounded contexts and their relationships to one another. |
| Shared Kernel | Part of the model that is shared by two or more teams, who agree not to change it without collaboration |
Code Classes, Models and Objects
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Anemic Domain Model | Model with classes focused on state management, good for Create, read, update and delete (CRUD) |
| Rich Domain Model | Model with logic focused on behavior, not just state, this is preferred for DDD. |
| Entity | A mutable class (liable to change) with an identity that is not tied to its property values which is used for tracking and persistence. |
| Immutable | Type whos state cannot be changed once the object is instantiated (think private setters that you can only access in the constructor) |
| Value Object | An immutable class which identity is defined by the combination of its values. |
| Domain Services | A place in the model to hold behavior that doesn’t belong elsewhere in the domain. |
| Side Effects | State change of the application or interaction with infrastructure in the outside world. |
Aggregates
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Aggregate | A transactional graph of objects |
| Aggregate Root | The entry point of an aggregate which ensures the integrity of the entire graph |
| Invariant | A condition that should always be true for the system to be in a consistent state |
| Persistence Ignorant Classes | Classes that have no knowledge about how they are persisted |
Repositories
A repository represents all objects of a certain type as a conceptual set…like a collection with more elaborate querying capability. —Eric Evans
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Repository | A class that encapsulates the data persistence for an aggregate root |
| ACID | Atomic, Consistent, Isolated, and Durable |
Domain Events
Decoupling the Domain Model’s Communications.
Use a Domain Event to capture an occurrence of something that happened in the domain. —
Vaughn Vernon
Example events:
- User Authenticated
- Appointment Confirmed
- Payment Received
Designing Domain Events:
- Each event is its own class
- Include when the event took place
- Capture event-specific details
- Event fields are initialized in constructor
- No behavior or side effects
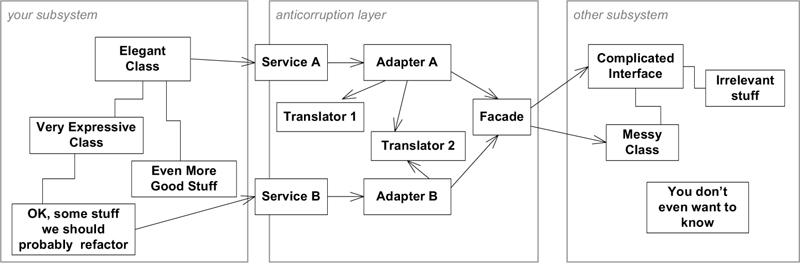
Anti-Corruption Layers
Translate between foreign systems’ models & our own using design patterns
- Facade
- Adapter
- custom translation classes or services
The structure of an Anti-Corruption Layer:
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Domain Event | A class that captures the occurrence of an event in a domain object |
| Hollywood Principle | “Don’t call us, we’ll call you” |
| Inversion of Control (IOC) | A pattern for loosely coupling a dependent object with an object it will need at runtime |
| Anti-Corruption Layer | Functionality that insulates a bounded context and handles interaction with foreign systems or contexts |
References
- https://www.pluralsight.com/courses/domain-driven-design-fundamentals
- https://dddcommunity.org/
- https://www.infoq.com/domain-driven-design/