Sweet so K8’s is Kubernetes right, so whats K3’s? Simple answer - Its lightweight Kubernetes for ARM processors which run on Raspberry Pi’s <3 I was inspired by Jeff Geerling’s Turing Pi Cluster videos to try do more with my Pi 4 boards!
Kubernetes comes in many distributions and flavours as show by the CNCF Cloud Native Landscape (the group that maintains kubernetes). I have chosen to focus on K3S by Rancher Labs which has an extremely light footprint thanks to the amazing work by Darren Shepherd (Chief Architect at Rancher Labs).
“We wanted an installation of Kubernetes that was half the size in terms of memory footprint. Kubernetes is a 10-letter word stylized as K8s. So something half as big as Kubernetes would be a 5-letter word stylized as K3s. There is no long form of K3s and no official pronunciation. rancher.com”
K3S Kubernetes ecosystem
Kubernetes has the following common terms:
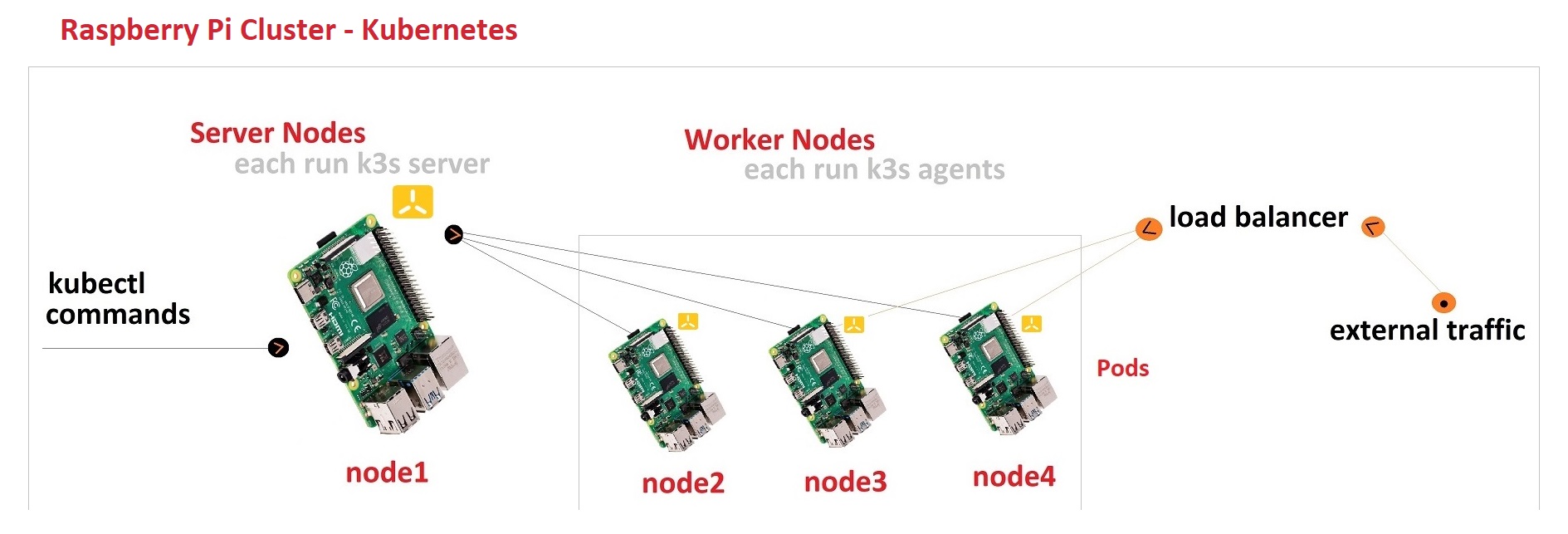
- K3S Server
- -The server node that handles the
kubectlcommands - -There can be several server nodes.
- -Also known as
master - -Runs the
k3s server - K3S Agent
- -The worker node, there can be several worker nodes.
- -Runs the
k3s agent - Container
- -This is a running
Docker Imagelike carlpaton/nginx-pi-demo - Pods
- -This is the
Kubernetes ecosystemrunning on a node which is running containers. - -Note the containers dont necessarily need to be contributing to a common goal to be considered part of the pod.
- Node
- -This is the machine that runs and instance of
Kubernetes, this can be a Virtual Machine, PC, Laptop or in my case a Raspberry Pi. - Cluster
- -This is several
Nodesconnected to gether on the same network.
Setup Hardware and OS
I used the same OS Steps (For Cluster) steps and used the image 2020-08-20-raspios-buster-armhf-lite.
Then, this cluster has two nodes:
node1(server node) ~ runs thek3s servernode3(worker node) ~ runs thek3s agent
Setup Passwordless SSH Access
See the No passphrase section on this passwordless SSH access post.
Setup K3s
This can either be done manually (on each node) or with a Playbook.
Setup K3s (Manual)
Enable container features in the kernel:
node1 and node3
1 | sudo -i |
Then add cgroup_enable=cpuset cgroup_memory=1 cgroup_enable=memory to the end, then reboot
1 | sudo reboot |
Using a utility script from Rancher Labs run the followng curl command:
node1
1 | curl -sfL https://get.k3s.io | sh -s - --write-kubeconfig-mode 644 ~ install |
You will then see [INFO] systemd: Starting k3s. To get the join key:
1 | sudo cat /var/lib/rancher/k3s/server/node-token |
node3
Im not sure why the script below doesnt start the worker K3S agent but it does install and configure it.
1 | export K3S_URL="https://192.168.1.79:6443" |
You will then see [INFO] systemd: Starting k3s-agent
I had to then manually start the agent:
1 | sudo k3s agent --server ${K3S_URL} --token ${K3S_TOKEN} |
The problem with this is when the SSH session is closed the agent is terminated too. I fixed this by creating a system service.
node1
After that all the nodes started up and made a cluster automagically <3
1 | kubectl get node -o wide |
Setup K3s (Playbook)
THIS DID NOT WORK FOR ME :( #sad
I tried to followed Jeff’s advice and use ansible to manage all of the Raspberry Pi’s with this ansible playbook from Rancher Labs.
node1
1 | sudo apt-get install git ansible |
Clone the playbook from Rancher labs and copy the inventory/sample folder to the name of your cluster. I called mine carl-cluster
1 | git clone https://github.com/rancher/k3s-ansible |
Set the hosts, these are your Raspberry Pi’s. You can use the IP or DNS.
1 | cd inventory/carl-cluster |
I used the following config
1 | [master] |
Set the pi user in group_vars
1 | cd group_vars |
Then run this command to install your cluster!
1 | cd ../../../ |
This was as far as I got with the playbook, running on node1 complained about not being able to see node1
1 | WIP - ACTUAL ERROR HERE |
Check whats running
1 | kubectl get pods --all-namespaces |
Cluster Monitoring
This Cluster Monitoring tool was built by Carlos Eduardo and he made it work for ARM based clusters.
Required software install
1 | apt-get update ~ update apt cache |
Switch to root and clone
1 | sudo su ~ switch to root user |
Setup
1 | cd cluster-monitoring |
Then update the following for K3S
1 | { |
1 | { |
1 | k3s: { |
1 | suffixDomain: '192.168.1.185.nip.io', ~ this was my worker node |
Finally build the mainfest for your cluster
1 | make vendor |
Now Kuberbettes will take all these things created though these manifests and start scheduling them on nodes. Some STATUS will be ContainerCreating as its pulling down docker images ect.
1 | kubectl get pods -n monitoring |
- http://grafana.192.168.1.185.nip.io/ ~ admin admin
- http://prometheus.192.168.1.185.nip.io/
- http://alertmanager.192.168.1.185.nip.io/
Get logs in pods, containers
1 | kubectl get namespaces |
unistall
1 | kubectl delete -f manifests/setup |